   |
Imidazolium dithiocarboxylates
Adducts of CS2 to
imidazol-2-ylidenes, N,N′-dialkyl-4,5-dimethylimidazolium-2-dithio-carboxylates
(alkyl = CH3, C2H5, i-C3H7)
Coworkers in this project:Stefan DümmlingThis project relied on a cooperation with Norbert Kuhn (Institut für Anorganische Chemie). Oral presentations:Bernd Speiser at thePublications from this project:S. Dümmling, B. Speiser, N. Kuhn und G. Weyers, Acta Chem. Scand., 53, 876 - 886 (1999); Two-Electron-Transfer Redox Systems. Part 3. Electrochemical Reduction of N,N′-Dialkyl-4,5-dimethylimidazolium-2-dithiocarboxylates to 1,1-Dithiolate Anions in THF. Steric Modulation of Potential Ordering by Substituents.N. Kuhn, G. Weyers, S. Dümmling, und B. Speiser, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon 128, 45 - 62 (1997); Derivate des Imidazols. 25. Reduktion von Carben-Addukten des Kohlenstoffdisulfids: ein neuer Weg zu elektronenreichen 1,1-Dithiolaten.
|
| © AG Speiser 2011 | |
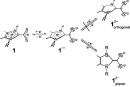 are reduced to dianions (1,1-dithiolates) in a two-step process. The size of the
alkyl ligands modulates the relative formal redox potentials of the two steps,
leading to an inverted potential situation for the i-C3H7-derivative.
In the latter case, the second reduction occurs at less negative potentials as the first one.
The steric effect is explained by the structural changes occuring during reduction (arrangement of heterocyclic ring and CS2
fragment changes from orthogonal to planar).
are reduced to dianions (1,1-dithiolates) in a two-step process. The size of the
alkyl ligands modulates the relative formal redox potentials of the two steps,
leading to an inverted potential situation for the i-C3H7-derivative.
In the latter case, the second reduction occurs at less negative potentials as the first one.
The steric effect is explained by the structural changes occuring during reduction (arrangement of heterocyclic ring and CS2
fragment changes from orthogonal to planar).