   |
Redoxactive Nanoparticles
"Chemistry in Interphases" characterizes
the attempt to immobilize reactive centers on a solid or polymeric support.
Advantageous properties of homogeneous and heterogeneous processes (e.g.,
catalysis) are expected to be combined in such systems.
If the centers are also redox active, the resulting materials can be characterized in detail
by electrochemical techniques.
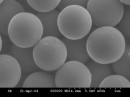
A particular support is silica, which is prepared by the sol-gel reaction and
modified with reactive centers. In the present project, we use spherical, non-porous, higly
monodisperse silica particles (Stöber particles) which have diameters
of several 100 nm. Coworkers in this projectAnna Budny, Filip Novak, Nicolas Plumeré, Diana Straub, Bernd Schetter, Ines Dreiling, Judith Schäfer, Tina Wener, Andreas Schank, Adrian Ruff and Thomas ReißigWe cooperate with the groups in the Graduiertenkolleg and Prof. B. Børresen, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway. We acknowledge funding of this project by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bonn - Bad Godesberg (within the Graduiertenkolleg "Chemie in Interphasen"), the Stiftung Stipendien-Fonds (Fonds der Chemie), Frankfurt a.M., and the Max-Buchner-Forschungsstiftung, Frankfurt a. M.. Poster presentationA. Ruff, M. Passon, P. Schuler, and B. Speiser, "Immobilization of viologen units by Si-C bond formation at Si-H terminated Stöber silica particles with d ≈ 230 nm and their electrochemical behavior at MPA modified gold electrodes", Electrochemistry 2012, München, GermanyA. Ruff, B. Speiser, and I. Dreiling, "Electrochemical behavior of viologen modified spherical silica particles at paraffin impregnated graphite electrodes", Electrochemistry 2012, München, Germany A. Ruff and B. Speiser, "Redox-active nanoparticles: Synthesis and electrochemical behavior of viologen modified Stöber silica particles with a diameter of 125 nm", ElecNano4 - 7th ECHEMS 2011, Paris, France Oral presentationsBernd Speiser at the 8th ECHEMS 2012, Bertinoro/I, June 28 - July 1, 2012Nicolas Plumeré at the Bernd Speiser at the Publications from this projectD.R. Abad, J. Henig, H.A. Mayer, T. Reißig und B. Speiser, Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. 9. Synthesis, Electrochemistry, and Diffusion Properties of Caged Octakis(N-ferrocenoyl-3-aminopropyl)silsesquioxane, Organometallics 33, 4777–4783 (2014).M. Passon, A. Ruff, P. Schuler, B. Speiser und I. Dreiling, Redox-active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 8. Stepwise solid-phase synthesis and solid state electrochemistry of redox active viologen core/shell structured modified silica materials, ChemElectroChem 1, 263-280 (2014). A. Ruff, B. Speiser, and I. Dreiling, Redox-active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 7. Redox behavior of core/shell structured viologen modified silica particles immobilized at paraffin impregnated graphite electrodes, J. Electroanal. Chem. 710, 10-16 (2013). A. Ruff, P. Schuler and B. Speiser, Erratum to: Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 6. Synthesis and spectroscopic and electrochemical characterization of viologen-modified Stöber silica particles with diameters of approximately 125 nm, J. Solid State Electrochem. 17, 1787 (2013). A. Ruff, P. Schuler and B. Speiser, Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 6. Synthesis and spectroscopic and electrochemical characterization of viologen-modified Stöber silica particles with diameters of approximately 125 nm, J. Solid State Electrochem. 17, 79-97 (2013). N. Plumere, A. Ruff, B. Speiser, V. Feldmann and H.A. Mayer, Redox-active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 5. Stöber Silica Particles as Basis for Redox-active Modifications: Particle Shape, Size, Polydispersity and Porosity, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 368, 208-219 (2012). F. Novak, N. Plumeré, B. Schetter, B. Speiser, D. Straub, H.A. Mayer, M. Reginek, K. Albert, G. Fischer, C. Meyer, H.-J. Egelhaaf and B. Børresen, Redox-active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 4. Synthesis, Size Distribution, and Electrochemical Adsorption Behavior of Ferrocene- and (Diamine)(diphosphine)-ruthenium(II)-modified Stöber Silica Colloidal Particles, J. Solid State Electrochem., 14, 289-303 (2010). N. Plumeré, B. Speiser, B. Dietrich, K. Albert, J.J. Pesek und M.T. Matyska, Thermally Induced Radical Hydrosilylation for Synthesis of C18 HPLC Phases from Highly Condensed Si-H Terminated Silica Surfaces, Langmuir, 25, 13481-13487 (2009). N. Plumeré, B. Speiser, H.A. Mayer, D. Joosten and L. Wesemann, Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 3. High-Temperature Chlorination-Reduction Sequence for the Preparation of Silicon Hydride Modified Silica Surfaces, Chem. Eur. J., 15, 936-946 (2009). N. Plumereré and B. Speiser, Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 2. Photochemical Hydrosilylation on a Hydride Modified Silica Particle Surface for the Covalent Immobilization of Ferrocene, Electrochim. Acta, 53, 1244 - 1251 (2007). A. Budny, F. Novak, N. Plumeré, B. Schetter, B. Speiser, D. Straub, H.A. Mayer and M. Reginek, Redox-Active Silica Nanoparticles. Part 1. Electrochemistry and Catalytic Activity of Spherical, Nonporous Silica Particles with Nanometric Diameters and Covalently Bound Redox-active Modifications, Langmuir, 51, 10605 - 10611 (2006).
|
| © AG Speiser 2014 | |